JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data exchange format.
If you're not yet familiar with JSON, you can first check out our JSON tutorial.
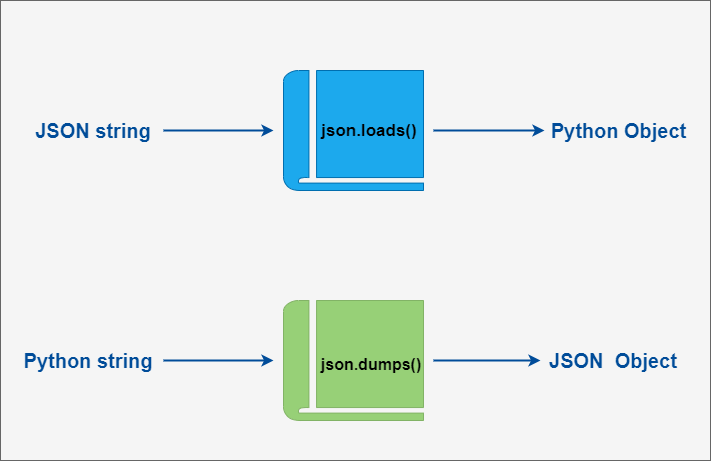
In Python 3, you can use the json module to encode and decode JSON data. It contains two key functions:
json.dumps(): Encodes data.json.loads(): Decodes data.
During the encoding and decoding of JSON, Python's primitive types will convert to and from JSON types according to the following mappings:
Python to JSON Type Conversion Table:
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
dict | object |
list, tuple | array |
str | string |
int, float, derived Enums | number |
True | true |
False | false |
None | null |
JSON to Python Type Conversion Table:
| JSON | Python |
|---|---|
| object | dict |
| array | list |
| string | str |
| number (int) | int |
| number (real) | float |
| true | True |
| false | False |
| null | None |
json.dumps and json.loads Example
Below is an example that demonstrates how to convert Python data structures to JSON:
Example (Python 3.0+)
#!/usr/bin/python3
import json
# Python dictionary converted to JSON object
data = {
'no': 1,
'name': 'PMeve',
'url': 'https://www.pmeve.com'
}
json_str = json.dumps(data)
print("Original Python data:", repr(data))
print("JSON object:", json_str)Output:
Original Python data: {'no': 1, 'name': 'PMeve', 'url': 'https://www.pmeve.com'}
JSON object: {"no": 1, "name": "PMeve", "url": "https://www.pmeve.com"}From the output, you can see that the encoded version is quite similar to its original repr() representation.
Continuing with the previous example, we can now convert a JSON-encoded string back to a Python data structure:
Example (Python 3.0+)
#!/usr/bin/python3
import json
# Python dictionary converted to JSON object
data1 = {
'no': 1,
'name': 'PMeve',
'url': 'http://www.pmeve.com'
}
json_str = json.dumps(data1)
print("Original Python data:", repr(data1))
print("JSON object:", json_str)
# Convert JSON object back to Python dictionary
data2 = json.loads(json_str)
print("data2['name']: ", data2['name'])
print("data2['url']: ", data2['url'])Output:
Original Python data: {'name': 'PMeve', 'no': 1, 'url': 'http://www.pmeve.com'}
JSON object: {"name": "PMeve", "no": 1, "url": "http://www.pmeve.com"}
data2['name']: PMeve
data2['url']: http://www.pmeve.comIf you're dealing with files instead of strings, you can use json.dump() and json.load() to encode and decode JSON data. For example:
Example (Python 3.0+)
# Write JSON data
with open('data.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(data, f)
# Read JSON data
with open('data.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)For more details, please refer to the official Python documentation on JSON.