Heapsort in Python
Heapsort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a binary heap data structure. A heap is a nearly complete binary tree that satisfies the heap property, meaning that the key or index of each child node is always smaller (or larger) than the key or index of its parent. Heapsort is a selection sort that leverages the heap data structure to perform sorting.
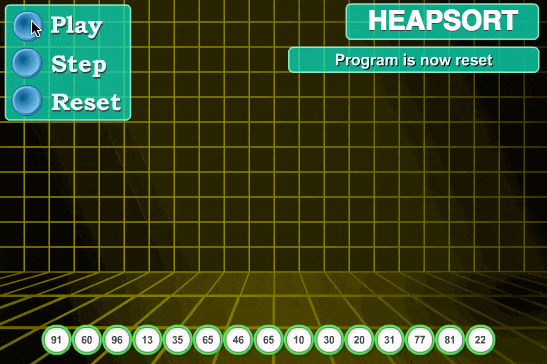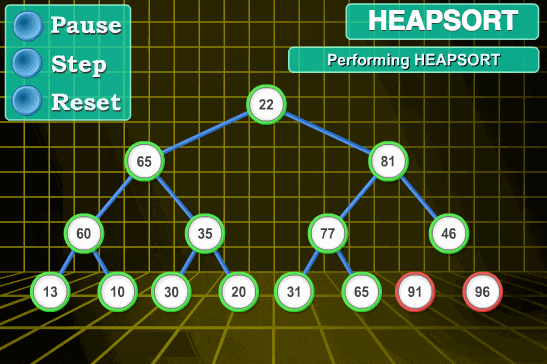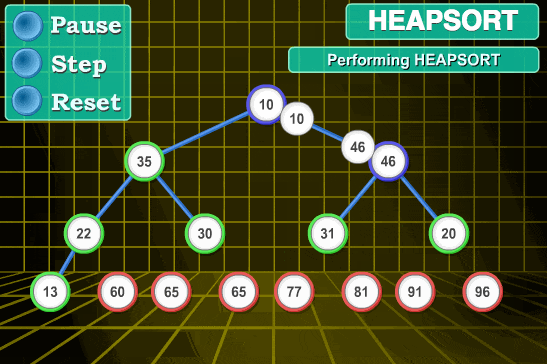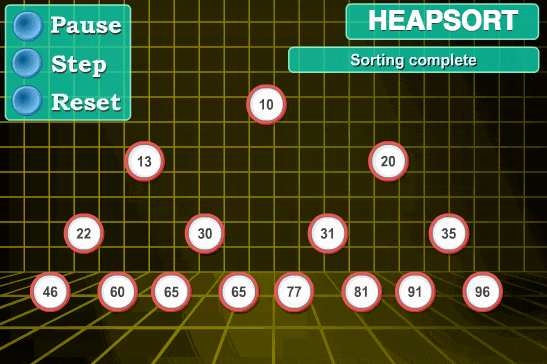
Example:
# Function to heapify a subtree rooted with node i, n is the size of the heap
def heapify(arr, n, i):
largest = i # Initialize largest as root
l = 2 * i + 1 # Left child index = 2*i + 1
r = 2 * i + 2 # Right child index = 2*i + 2
# If the left child exists and is greater than root
if l < n and arr[i] < arr[l]:
largest = l
# If the right child exists and is greater than largest so far
if r < n and arr[largest] < arr[r]:
largest = r
# If largest is not root
if largest != i:
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i] # Swap
# Heapify the root
heapify(arr, n, largest)
# Main function to perform heapsort
def heapSort(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Build a maxheap
for i in range(n, -1, -1):
heapify(arr, n, i)
# Extract elements from the heap one by one
for i in range(n-1, 0, -1):
arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i] # Swap the current root with the last element
heapify(arr, i, 0)
# Example array
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7]
heapSort(arr)
n = len(arr)
# Print the sorted array
print("Sorted array:")
for i in range(n):
print("%d" % arr[i], end=" ")Output:
Sorted array: 5 6 7 11 12 13
In this example, the array [12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7] is sorted using the Heapsort algorithm. After constructing a max heap and sorting the elements, the final sorted array is [5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13].