Counting Sort in Python
Counting sort is an algorithm that sorts by transforming the input data into keys and storing these keys in an auxiliary array. As a linear time complexity sorting algorithm, counting sort requires the input data to have a specific range of integers.
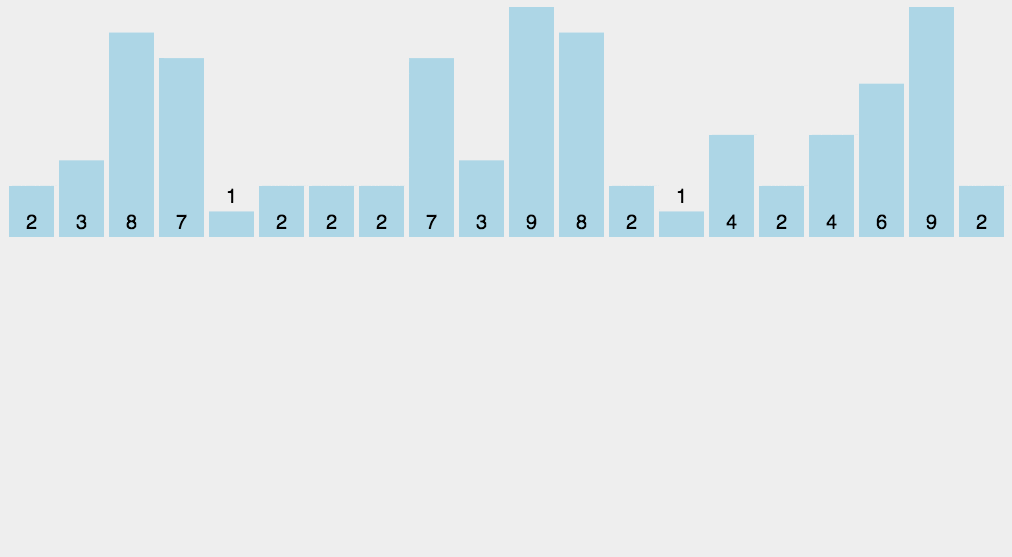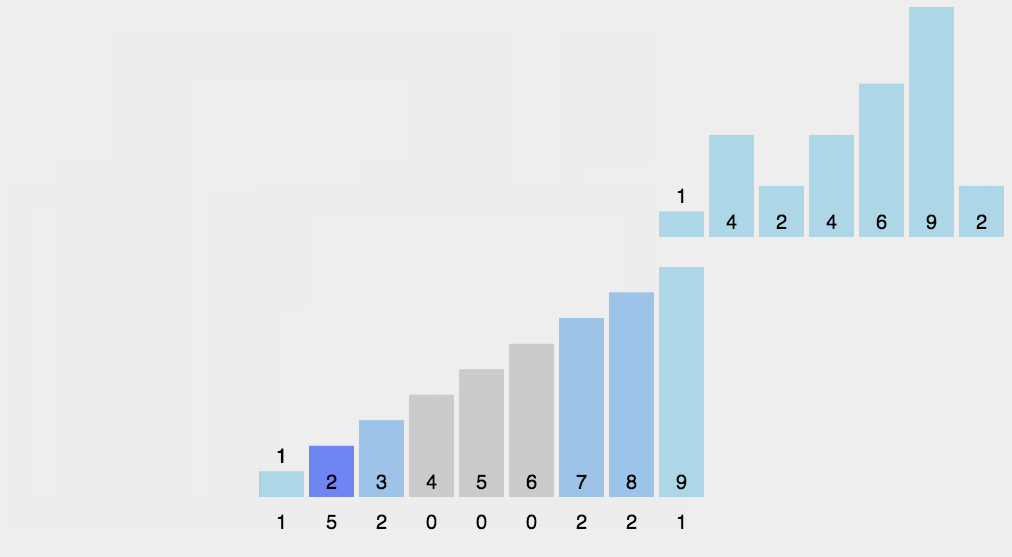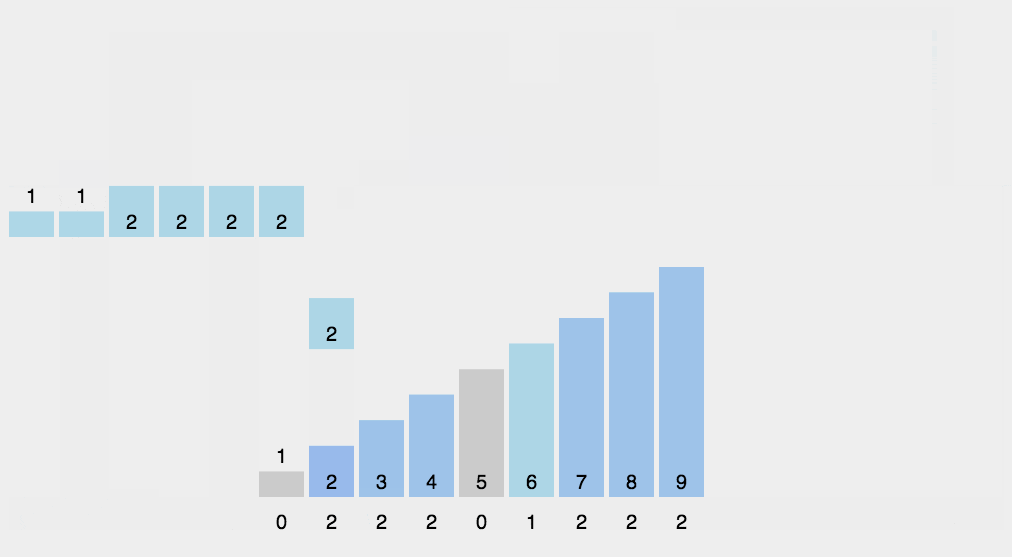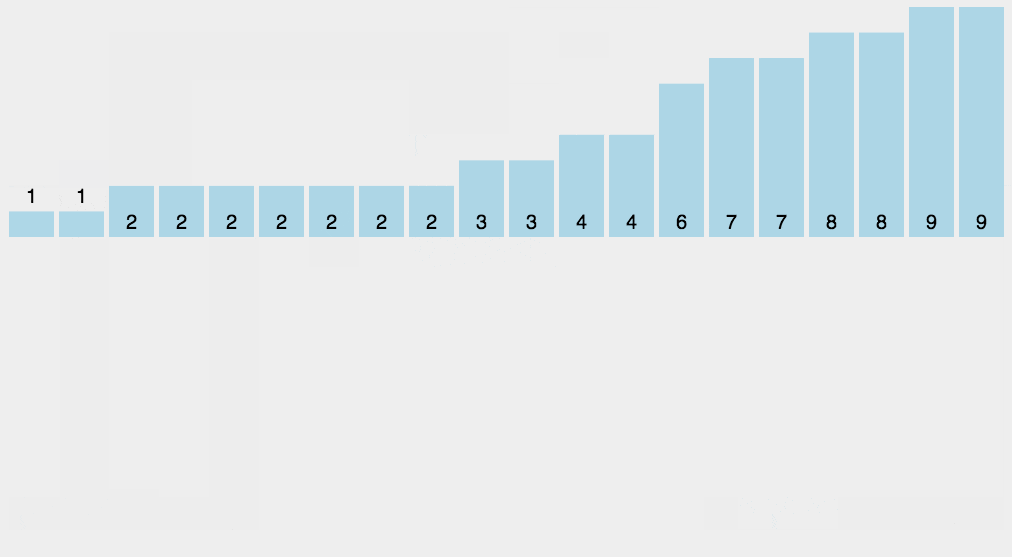
Example:
# Function to perform counting sort
def countSort(arr):
# Initialize output array
output = [0 for i in range(256)]
# Initialize count array with zero
count = [0 for i in range(256)]
# Initialize result array
ans = ["" for _ in arr]
# Store the count of each character
for i in arr:
count[ord(i)] += 1
# Store the cumulative count
for i in range(256):
count[i] += count[i - 1]
# Build the output character array
for i in range(len(arr)):
output[count[ord(arr[i])] - 1] = arr[i]
count[ord(arr[i])] -= 1
# Copy the sorted characters into ans array
for i in range(len(arr)):
ans[i] = output[i]
return ans
# Input string
arr = "wwwrunoobcom"
# Call countSort function
ans = countSort(arr)
# Print the sorted character array
print("Sorted character array: %s" % ("".join(ans)))Output:
Sorted character array: bcmnoooruwww
In this example, the string "wwwrunoobcom" is sorted using the counting sort algorithm. The sorted result is "bcmnoooruwww", where the characters are arranged in lexicographical order. Counting sort works efficiently for characters as they have a well-defined range, making this algorithm particularly useful for sorting strings.

