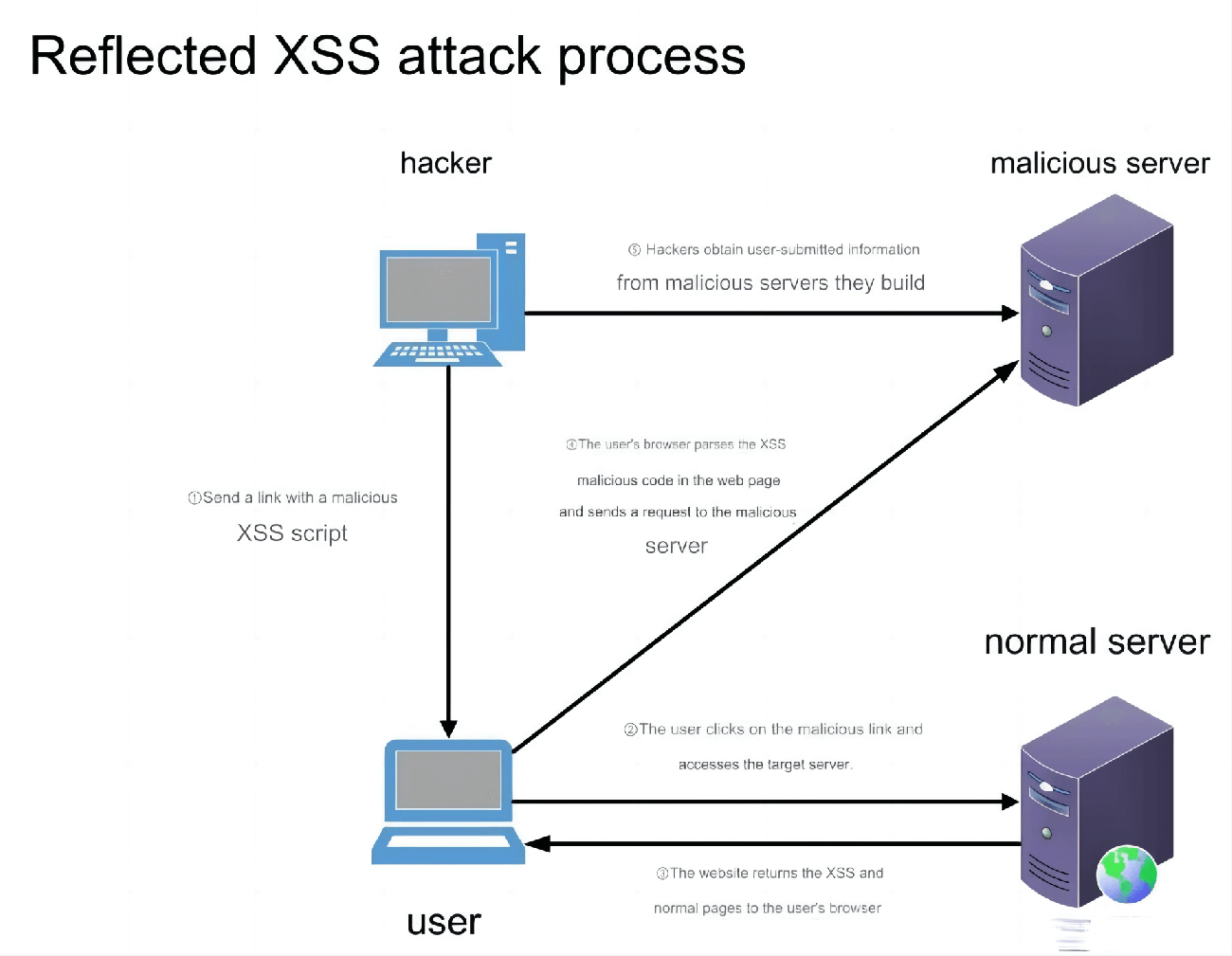
Have you ever wondered who might know about your late-night visits to websites like www.pmeve.com, besides your browser history and the dark, quiet night? To understand the answer, we first need to explore what happens when you access a website. This article will walk you through the journey of website visits and discuss how you can safely browse the web by using various security technologies.
How Internet Access Works:
If you were browsing a website 10 years ago, you would likely see a URL like http://www.pmeve.com in your browser's address bar. The "http" in front of the URL indicates that the website is using the HTTP protocol. Once you press enter, the process of accessing the website begins.
Every device on the internet is uniquely identified by an IP address, and the website you are visiting is hosted on a server with its own IP address. The first step in accessing a website is using DNS (Domain Name System) to map the domain name (the URL) to the server's IP address. The DNS is a service that helps convert human-readable URLs into IP addresses so that browsers can communicate with the server.
When the browser knows the IP address, it sends a TCP connection request to port 80 of that IP address, which then presents the website content to you. In short, using HTTP to visit a website involves these steps:
The browser requests the DNS server to translate the URL into an IP address.
The browser sends a TCP connection request to port 80 of that IP address.
The browser sends an HTTP request and receives the server’s HTTP response to render the webpage.
Privacy Concerns with HTTP:HTTP transmits data in plaintext, meaning anyone can intercept and view your information during the transfer. Essentially, your privacy could be completely exposed.
The Shift to HTTPS:Today, most websites use URLs like https://www.pmeve.com, with "https" indicating the HTTPS protocol, which stands for HTTP + TLS. While HTTP transmits data in plaintext, TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a security protocol that encrypts the communication between your browser and the server, hiding the content from third parties.
The steps to accessing a website using HTTPS are:
The browser requests the DNS server to translate the URL into an IP address.
The browser sends a TCP connection request to port 443 of the IP address, initiating the TLS handshake.
The browser verifies the server’s security certificate, negotiates encryption algorithms, and exchanges encryption keys.
The browser sends an encrypted HTTP request, receives an encrypted HTTP response, decrypts, and renders the webpage.
Is HTTPS Completely Secure?While HTTPS is encrypted, some aspects of website visits can still expose your activity. For instance:
DNS Queries: Even if HTTPS is used, DNS queries are typically unencrypted, meaning your visited websites can still be known.
Traffic Analysis: Encrypted data can still be analyzed by its size and packet patterns, potentially revealing which websites you are visiting.
Techniques for Safe Internet Access:With advances in traffic recognition technology and an increasing number of surveillance points in networks, total anonymity is nearly impossible. However, the following techniques can enhance the security of your internet usage:
VPN (Virtual Private Network): A VPN creates an encrypted communication channel, allowing you to send and receive data securely. It reroutes your traffic through remote servers, hiding your real IP address. VPN protocols like PPTP, L2TP, IPSec, and GRE are common. However, many VPN protocols are now detectable by traffic analysis.
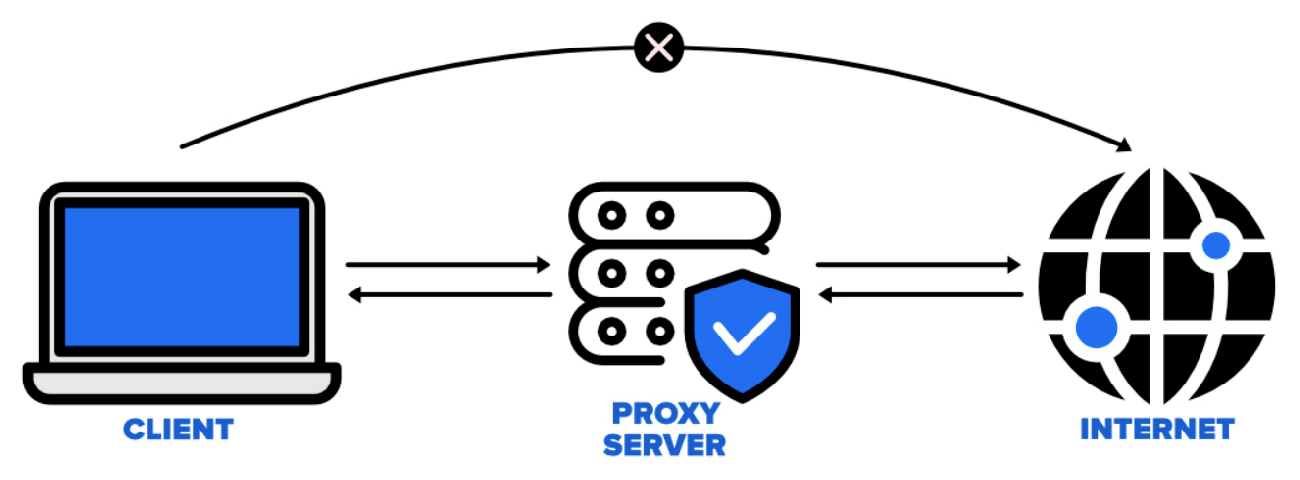
How VPN Works:VPN encrypts data and hides your real IP address, making your internet traffic invisible to potential monitors.
Proxy: A proxy acts as an intermediary between a client and a server. It allows users to send requests using the proxy server’s IP address instead of their own. However, proxies do not encrypt the data being transmitted, so additional encryption methods like traffic obfuscation are required. Obfuscation disguises data packets to make them less recognizable, often mimicking common network traffic patterns to evade detection.
Common Proxy Techniques:
Limitations of Proxies and Tor:Tor, despite its privacy features, can still be compromised if an attacker monitors both the entry and exit nodes, correlating traffic patterns to reveal user activity.
SOCKS5: A versatile protocol that handles all types of network traffic but sends data in plaintext.
Tor (The Onion Router): A decentralized network that encrypts requests three times and passes them through three nodes (entry, middle, and exit). Each node removes one layer of encryption, so no single node knows both the user and the destination website. However, due to multiple layers of encryption, Tor can slow down internet speeds.
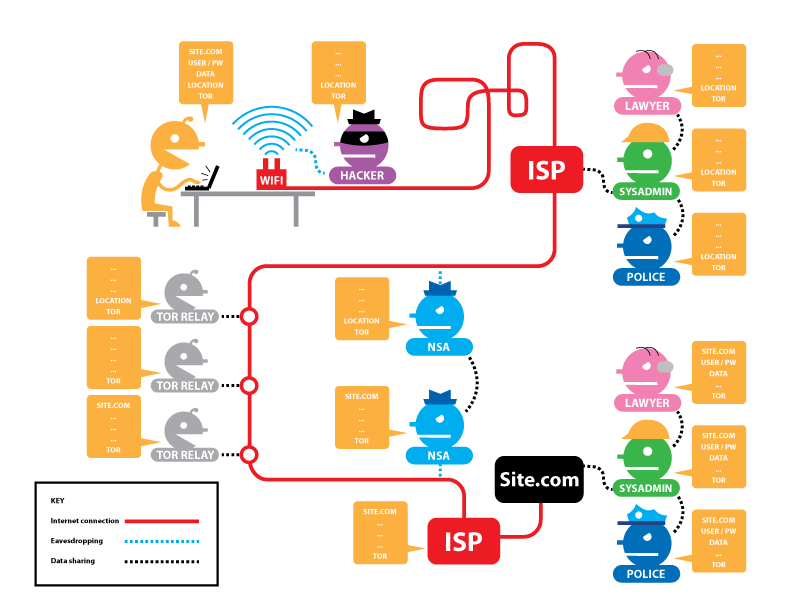
Conclusion:Accessing the internet safely requires using appropriate technologies like HTTPS, VPNs, and proxies. Each technology has its strengths and limitations, and it is essential to remember that absolute security does not exist on the internet.