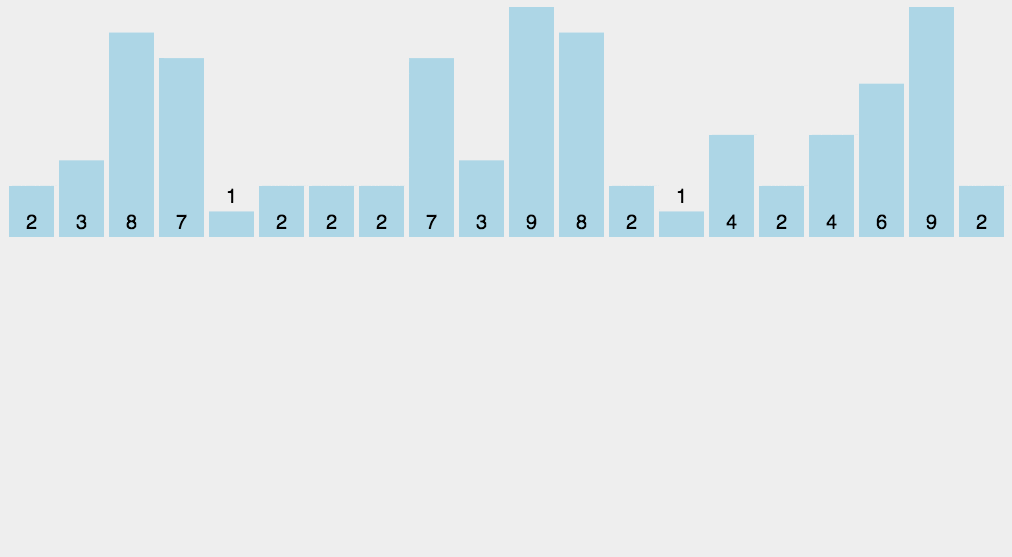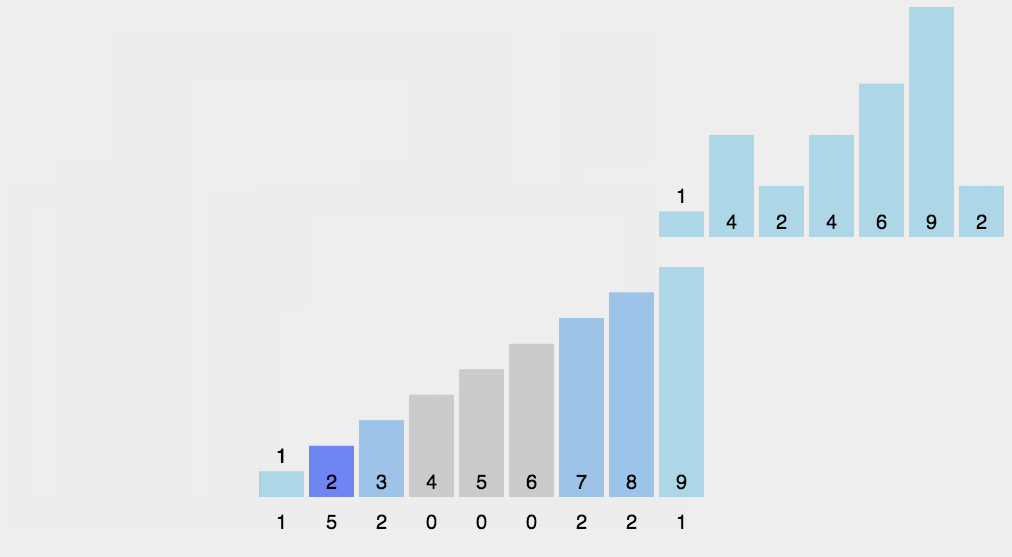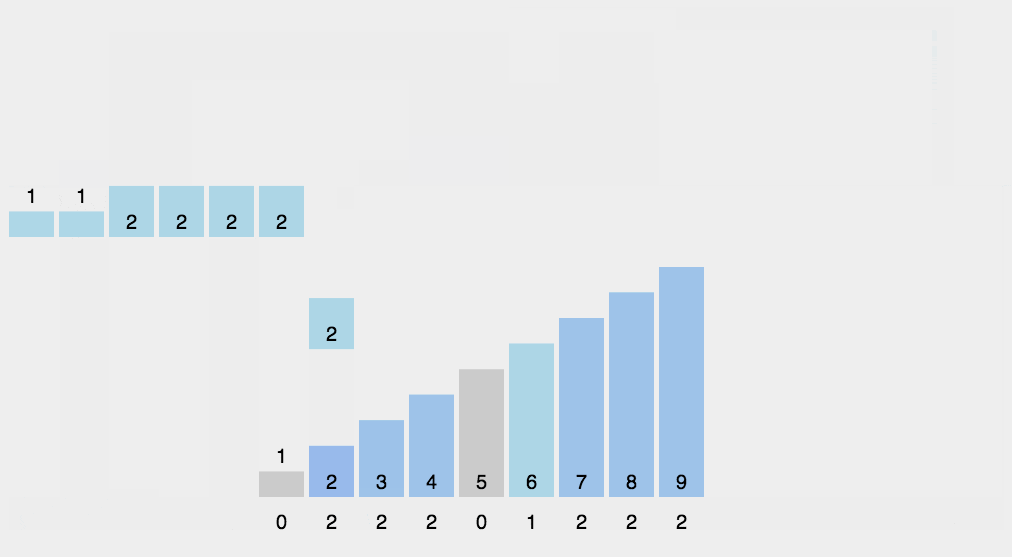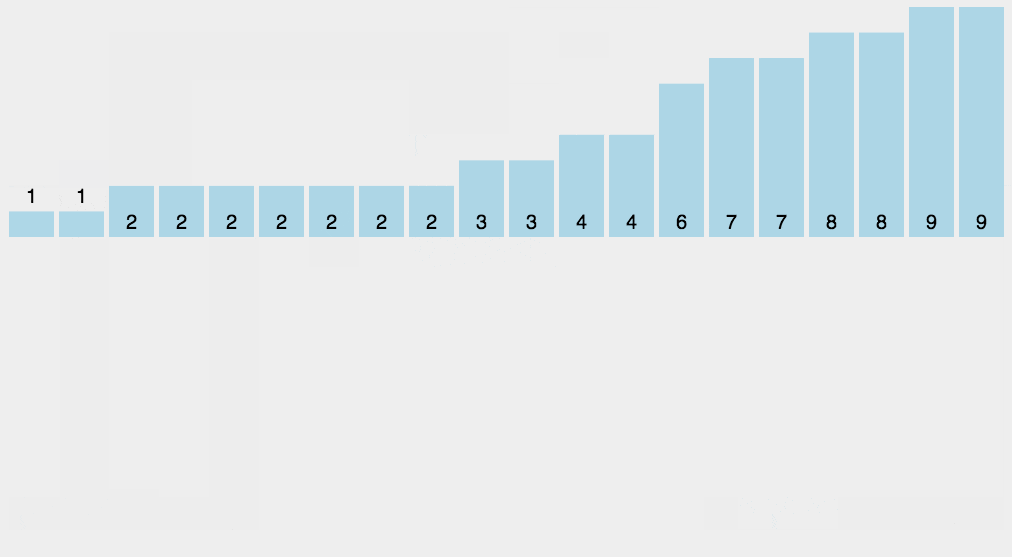Selection Sort in Python
Selection Sort is a simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. Its working principle is as follows:
First, it finds the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion of the array and places it at the beginning of the sorted portion. Then, it continues to find the next smallest (or largest) element from the remaining unsorted elements and places it at the end of the sorted portion. This process is repeated until all elements are sorted.
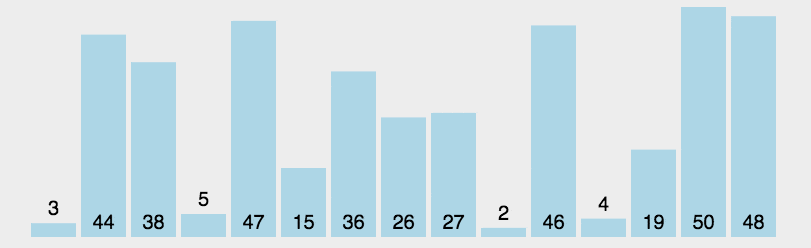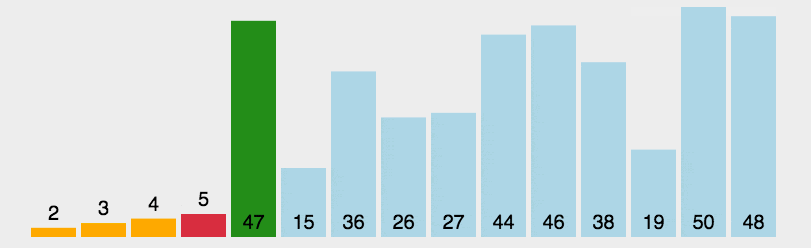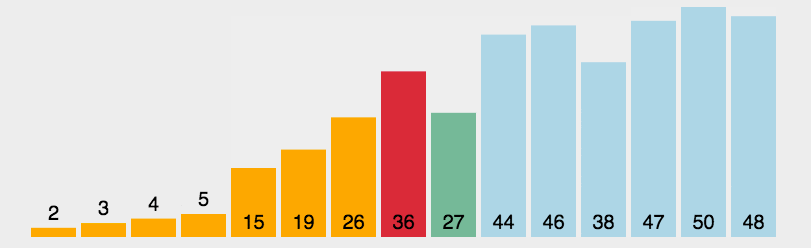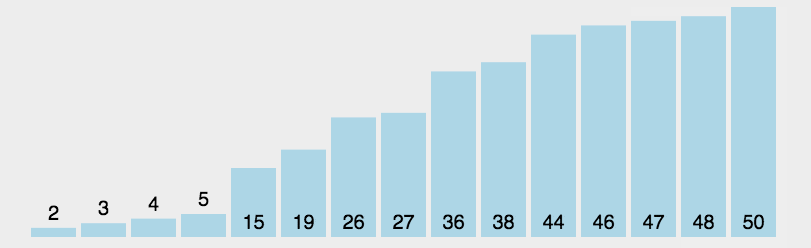
Example
Here is an implementation of Selection Sort in Python:
import sys
# Example array
A = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
# Traverse through all array elements
for i in range(len(A)):
# Find the minimum element in the unsorted portion
min_idx = i
for j in range(i + 1, len(A)):
if A[min_idx] > A[j]:
min_idx = j
# Swap the found minimum element with the first element of the unsorted portion
A[i], A[min_idx] = A[min_idx], A[i]
# Print the sorted array
print("Sorted array:")
for i in range(len(A)):
print("%d" % A[i])Output:
Sorted array: 11 12 22 25 64
In this example, the array [64, 25, 12, 22, 11] is sorted using the Selection Sort algorithm. The final sorted array is [11, 12, 22, 25, 64]. The algorithm repeatedly finds the smallest element from the unsorted part and places it in the correct position, ensuring a fully sorted array at the end.