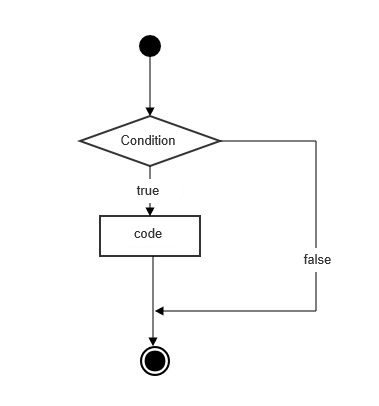
Bubble Sort in Python
Bubble Sort is another simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. It repeatedly traverses the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. This process is repeated until no further swaps are required, which means the list is fully sorted. The name "bubble" comes from the way smaller elements "bubble" to the top of the list through the series of swaps.
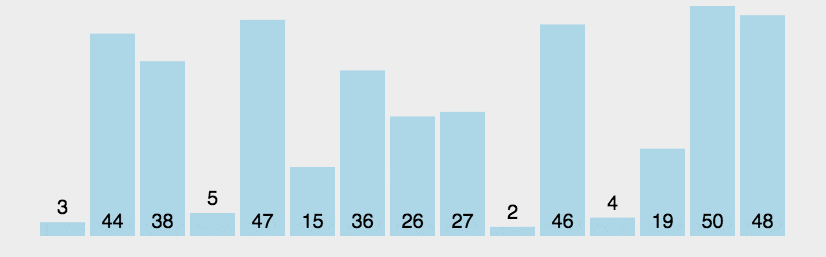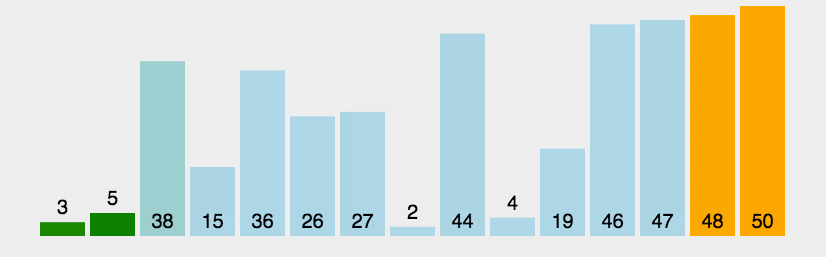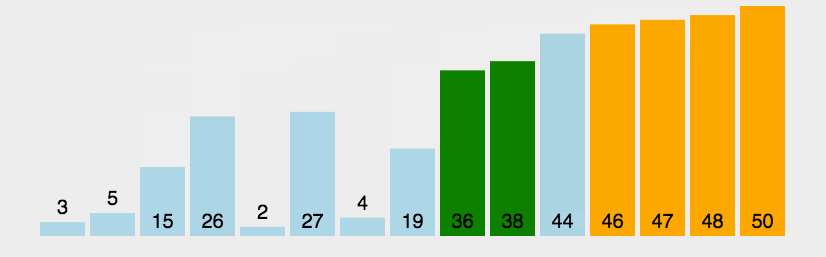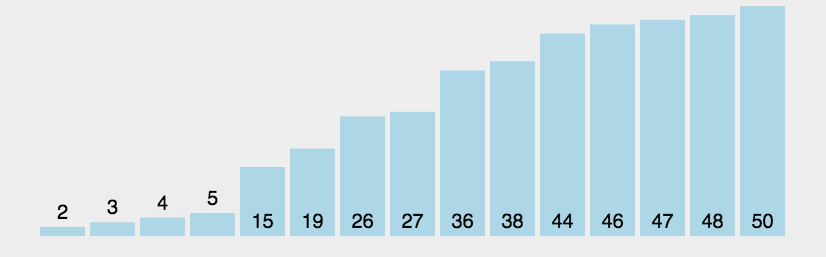
Example
Here is an implementation of Bubble Sort in Python:
def bubbleSort(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Traverse through all array elements
for i in range(n):
# The last i elements are already in place
for j in range(0, n-i-1):
# Swap if the element found is greater than the next element
if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:
arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
# Example array
arr = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
# Calling the bubble sort function
bubbleSort(arr)
# Print the sorted array
print("Sorted array:")
for i in range(len(arr)):
print("%d" % arr[i])
Output:
Sorted array: 11 12 22 25 34 64 90
In this example, the array [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90] is sorted using the Bubble Sort algorithm. After repeatedly comparing and swapping adjacent elements, the final sorted array becomes [11, 12, 22, 25, 34, 64, 90]. This method ensures that smaller elements gradually move to the top of the list.