Shell Sort in Python
Shell sort, also known as the decremental increment sort algorithm, is a more efficient version of insertion sort. However, Shell sort is a non-stable sorting algorithm.
The basic idea of Shell sort is to first divide the entire sequence of records to be sorted into several sub-sequences, each of which is sorted using direct insertion sort. Once the records in the entire sequence are "almost sorted," a final direct insertion sort is performed on the whole sequence.
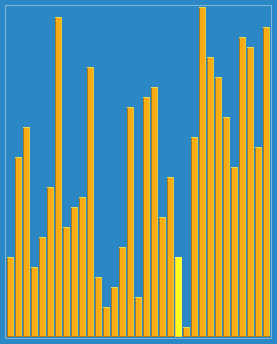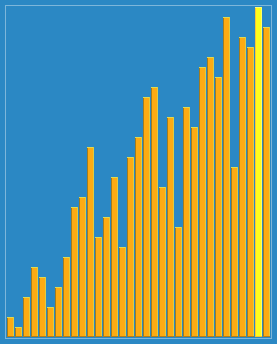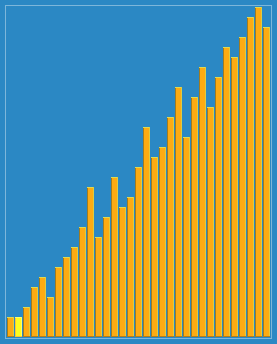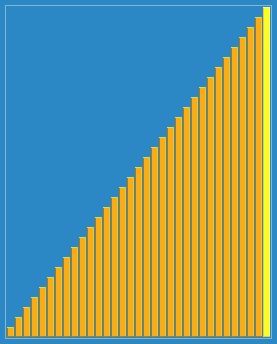
Example:
# Function to perform Shell sort
def shellSort(arr):
n = len(arr)
gap = int(n / 2)
while gap > 0:
for i in range(gap, n):
temp = arr[i]
j = i
while j >= gap and arr[j - gap] > temp:
arr[j] = arr[j - gap]
j -= gap
arr[j] = temp
gap = int(gap / 2)
# Input array
arr = [12, 34, 54, 2, 3]
n = len(arr)
print("Before sorting:")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i])
# Perform Shell sort
shellSort(arr)
print("\nAfter sorting:")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i])Output:
Before sorting: 12 34 54 2 3 After sorting: 2 3 12 34 54
In this example, the array [12, 34, 54, 2, 3] is sorted using the Shell sort algorithm. The result is [2, 3, 12, 34, 54], showing that Shell sort effectively improves upon basic insertion sort by reducing the number of comparisons and shifts needed to sort the array.