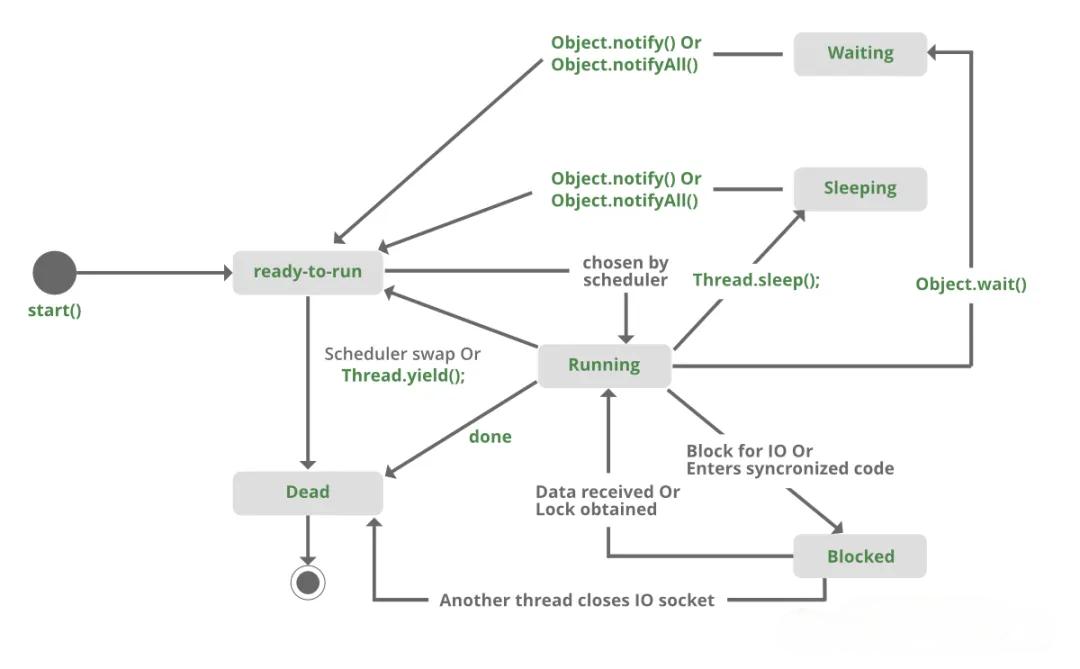
In a multi-threaded environment, it is essential to ensure that a code block can only be accessed by one thread at a time. Today, distributed architectures are popular within companies, so how do we ensure thread synchronization across different nodes in a distributed environment?
In distributed scenarios, we can use a distributed lock, which is a method to control mutual exclusion access to shared resources across a distributed system. For each lock, it’s crucial to have a unique ID to prevent erroneous unlocking (e.g., if locks A and B have the same key, and B unlocks at the exact moment A expires, without validating the lock ID, A could mistakenly be unlocked).

Redis offers the SETNX (Set if Not Exists) command, which inserts a value only if the key does not exist. Starting with Redis version 2.6.12, the SET command was overloaded to support inserting a value with an expiration time if the key does not exist. Although Redis doesn't provide a command to delete a key only when the value matches, version 2.6.0 introduced EXAL, which can be used to write scripts that enable this functionality.
Introducing dependencies
using ServiceStack.Redis;
Lock implementation process
private static readonly string ScriptSetIfAbsent = "return redis.call('SET',KEYS[1],ARGV[1],'EX',ARGV[2],'NX')";
private static readonly string ScriptDeleteIfEqualValue = @"if redis.call('GET',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then
return redis.call('DEL',KEYS[1])
else
return 'FALSE'
end";/// <summary>
/// Acquire a lock.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">Lock key</param>
/// <param name="lockToken">Lock token, used for releasing the lock</param>
/// <param name="lockExpirySeconds">Lock expiration time (in seconds)</param>
/// <param name="waitLockSeconds">Time to wait for the lock (in seconds)</param>
/// <returns>True if lock acquired successfully</returns>
public bool Lock(string key, out string lockToken, int lockExpirySeconds = 10, double waitLockSeconds = 0)
{
int waitIntervalMs = 1000;
string lockKey = GetLockKey(key);
DateTime begin = DateTime.Now;
string uuid = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
// Loop to acquire the lock
while (true)
{
string result;
using (var client = GetNativeClient())
{
// Return result of the SET operation, "OK" indicates success
result = client.EvalStr(ScriptSetIfAbsent, 1,
System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(lockKey),
System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(uuid),
System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(lockExpirySeconds.ToString()));
}
if (result == "OK")
{
lockToken = uuid;
return true;
}
// Stop waiting if the wait time is exceeded
if ((DateTime.Now - begin).TotalSeconds >= waitLockSeconds) break;
Thread.Sleep(waitIntervalMs);
}
lockToken = null;
return false;
}/// <summary>
/// Release the lock after executing the code
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">Lock key</param>
/// <param name="lockToken">Lock token</param>
/// <returns>True if lock is successfully released</returns>
public bool DelLock(string key, string lockToken)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(lockToken))
{
throw new Exception("The parameter lockToken cannot be null");
}
string lockKey = GetLockKey(key);
using (var client = GetNativeClient())
{
// Return number of deleted rows, 1 indicates success
string result = client.EvalStr(ScriptDeleteIfEqualValue, 1,
System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(lockKey),
System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(lockToken));
return result == "1";
}
}Lock usage process
if (RedisManager.Lock(key, out tokenLock))
{
try
{
IRedisClient rdsclient = null;
try
{
// Execute your business logic here
}
finally
{
rdsclient?.Dispose();
}
}
finally
{
RedisManager.DelLock(key, tokenLock);
}
}