At AWS re:Invent 2024, Amazon introduced a host of groundbreaking cloud computing technologies and AI solutions, including model distillation, upgrades to Amazon Q Developer, and the new P6 instances. This article explores how AWS empowers enterprises to modernize applications, enhance performance, reduce costs, and drive innovation for high-density AI workloads.
After Spending $8 Billion, Amazon "Ties the Knot" with Anthropic to Build the World's Largest AI Compute Cluster
The world's largest cloud computing giant is pulling out its hardcore resources!
At the annual cloud computing industry event, AWS re:Invent, AWS (Amazon Web Services) announced six new large models, previewed two upcoming ones, and introduced its 3nm third-generation AI training chip, Trainium3, and its most powerful AI server to date, Trn2 UltraServer. This is the first time the Amazon Nova series foundational models have been unveiled.

The models include four versions of language models: Micro, Lite, Pro, and Premier, as well as an image generation model, Canvas, and a video generation model, Reel. Currently, Reel supports generating 6-second videos, with plans to extend it to 2 minutes soon.

Amazon's President and CEO, Andy Jassy, revealed that next year, AWS will not only release a speech-to-speech model but also a more advanced Any-to-Any model—capable of processing and outputting text, images, audio, video, and other modalities.
These models will all be available in Bedrock, with customization and distillation options.
Additionally, AWS CEO Matt Garman announced the launch of the latest generative AI instance, Amazon EC2 Trn2, which offers 30%-40% better cost performance than current GPU-based EC2 instances.
Benoit Dupin, Apple’s Director of Machine Learning and AI, attended the event and shared that Apple has widely adopted Amazon's services across iPad, Apple Music, Apple TV, News, App Store, Siri, and other products and services.
He particularly noted that, compared to x86 instances, Apple has achieved over a 40% efficiency improvement in machine learning inference workloads using AWS chips like Amazon Graviton and Inferentia, and expects a 50% improvement when pretraining models on Trainium 2.

Anthropic, which Amazon invested $8 billion in, announced a collaboration with AWS to build the world’s largest compute cluster for machine learning training. The next generation of its Claude large models will be trained on a cluster powered by hundreds of thousands of Trainium2 chips.
Overall, AWS has rolled out major updates across its four key areas: computing, storage, databases, and AI inference.
1. The New Self-Developed Amazon Nova Series Models: Text, Image, and Video All in One
Andy Jassy, President and CEO of Amazon, shared how generative AI is now integrated across different Amazon businesses, improving efficiency and user experience in areas like e-commerce customer service, seller detail pages, inventory management, robotics, Alexa, Amazon Lens, online shopping size matching, and Prime Video.
He then unveiled the new Nova large model series!

Nova includes four language models:
Micro: A pure text model with a 128k context window, the lowest latency, and the fastest response speed.
Lite: A cost-effective multimodal model with a 300k context window that can quickly process image, video, and text inputs.
Pro: A multimodal model with a 300k context window, balancing accuracy, speed, and cost. It can understand video and generate creative materials.
Premier: Amazon’s most powerful multimodal model, capable of performing complex reasoning tasks, and ideal for distilling custom models (set to launch in Q1 2025).
It is stated that Micro, Lite, and Pro are at least 75% cheaper than the best-performing models in each category on Amazon Bedrock. They are also the fastest models in their respective categories on Bedrock.
AWS mentioned that by early 2025, some Nova models will expand their context windows to support over 2 million tokens.
In benchmark tests, the Micro version outperformed Gemini 1.5 Flash 8B and Llama 3.1 8B.
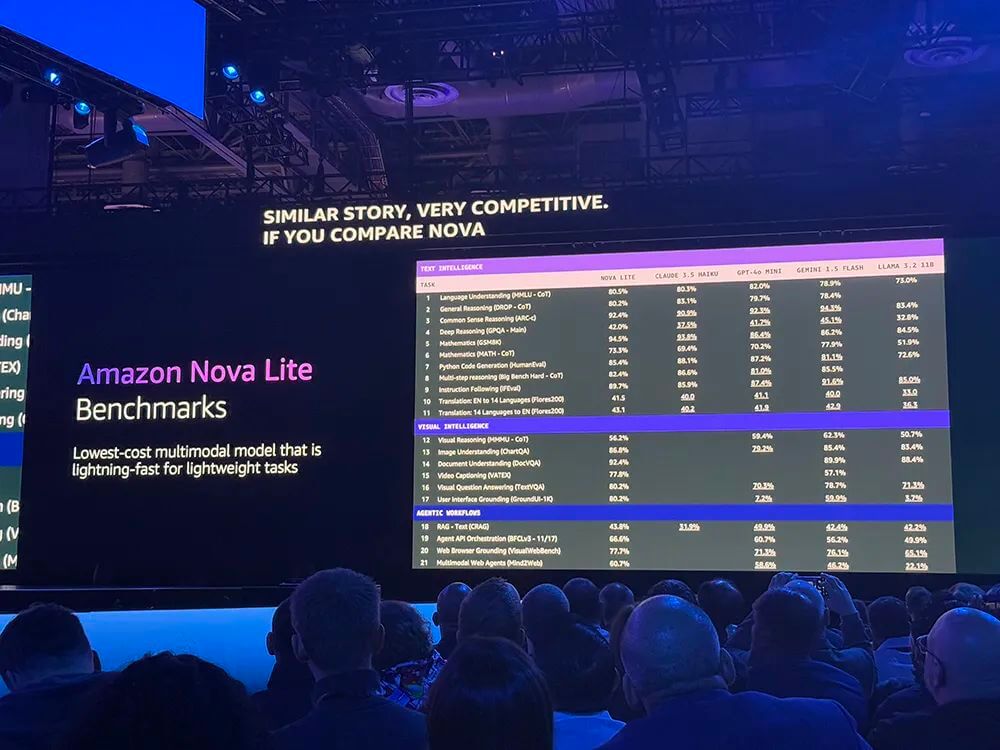
Lite is the lowest-cost multimodal model for lightweight tasks.
The newly released models include the image generation model Canvas and the video generation model Reel, both aimed at enhancing creative advertising content.
Canvas: Supports image generation and editing, offering color schemes, layout controls, built-in security features for traceable watermarks, and content moderation to prevent harmful content.
Reel: Generates 6-second videos based on keywords or optional reference images, with camera movement adjustments for panning, 360-degree rotation, and zooming. A 2-minute video version is coming soon.
These models support custom fine-tuning and distillation.

And here’s One More Thing: Next year, AWS will release two more Nova models: one is a "speech-to-speech" model, and the other is a powerful "Any-to-Any" multimodal model capable of processing text, images, audio, or video inputs and outputs, enabling the same model to perform various tasks.
2. Full Launch of AWS Trainium2 Instances, with the Third-Generation AI Training Chip and Most Powerful AI Server
AWS fully launched the Amazon EC2 Trn2 instances powered by the Trainium2 chip, offering 30%-40% better cost-performance than current GPU-based EC2 instances.

The new EC2 Trn2 instances are designed for high-performance deep learning training, including large language models and potential diffusion models.
AWS also unveiled a complete set of new AI hardware: the third-generation self-developed AI training chip Trainium3 and the most powerful AI server, the Trn2 UltraServer.
Third-Generation Self-Developed AI Training Chip
AWS released the next-gen AI training chip, Trainium3. It is the first AWS chip built using the 3nm process node, offering a 40% increase in energy efficiency and doubling performance.
The UltraServer powered by Trainium3 is expected to outperform the Trn2 UltraServer by 4 times. The first instances based on Trainium3 are expected to be available by the end of 2025.
The Most Powerful AI Server, Combining 64 Trainium2 Chips
AWS released the most powerful AI server to date, the Trn2 UltraServer, capable of supporting real-time inference for trillion-parameter AI models.
The new Trn2 UltraServer uses ultra-fast NeuronLink interconnect to connect four Trn2 servers, forming a giant server for faster large model training and inference.
Each Trn2 instance features 16 Trainium2 chips, delivering 20.8 PFLOPS, ideal for training and deploying large language models with billions of parameters.

The new EC2 Trn2 UltraServer connects 64 Trainium2 chips, providing up to 5 times the compute power and 10 times the memory compared to current EC2 AI servers, with FP8 peak performance expanding to 83.2 PFLOPS (4 times that of a single instance).
AWS has already conducted beta testing with early customers, including Adobe, AI software platform Poolside, data analysis platform Databricks, and Qualcomm.
Expanding Collaboration with Anthropic to Build the World’s Largest AI Compute Cluster
Tom Brown, co-founder and CTO of Anthropic, shared that, similar to Tetris, the tighter the machine’s internal structure, the cheaper and faster it is to run models. Over the past year, Anthropic’s performance engineering team has worked closely with Amazon and Annapurna teams to address this challenge.
He announced that AWS and Anthropic are collaborating on the construction of a project called "Project Rainier"—a Trn2 UltraServers EC2 UltraCluster. This cluster will expand distributed model training using hundreds of thousands of Trainium2 chips.
These chips, connected with a third-generation low-latency PB-scale EFA network, are five times more powerful than the petaflop performance used by Anthropic to train its current leading AI models.
Once completed, it is expected to become the largest AI compute cluster in the world, enabling Anthropic to build and deploy future models.
With Project Rainier, users will benefit from lower costs, faster speeds, and more intelligent, smarter agents.
Next-Gen AI Network Architecture: tnp10
The latest AI network architecture, tnp10, powers the Trainium2 UltraServer. AWS uses this network in both Trainium- and NVIDIA chip-based clusters, providing tens of PBs of network capacity to thousands of servers at 10-microsecond latency—enabling AWS’s fastest network expansion.
Tnp10’s large-scale parallelism, tight interconnection, and elasticity can scale from a few racks to clusters spanning multiple physical data center campuses.
The biggest source of failure in AI networks is optical links. AWS has been designing and running its custom optical systems for years to reduce failure rates continuously. To further optimize the network, AWS has introduced a new routing protocol in tnp10 called "Scalable Intent-Driven Routing (CIDR)," providing centralized planning, control, and optimization with decentralized speed and flexibility.
3. Three Major Updates to AWS Generative AI Platform Bedrock Services: Automated Reasoning Checks, Multi-Agent Collaboration, and Model Distillation
AWS Bedrock helps businesses build and scale generative AI applications. Today, three new features were announced: automated reasoning checks, multi-agent collaboration, and model distillation.
AWS has positioned Bedrock as "the easiest way to build generative AI applications." According to Matt Garman, thousands of customers use Bedrock for production applications daily, growing five times faster than last year.

Automated Reasoning Checks to Prevent AI Hallucinations
AI hallucinations are a key obstacle for AI applications in enterprise production. AWS discovered that automated reasoning can help address this issue. Automated reasoning is used to verify if systems function as intended. This tool can automatically check plans and software to validate how they respond to unexpected events.
As a result, AWS introduced AWS Automated Reasoning checks, which verify the accuracy of factual responses, generate auditable outputs, and show customers the exact reasoning behind a model’s conclusions.
At the same time, Amazon Bedrock will automatically set necessary rules to guide customers through iterative testing, ensuring models adjust to provide correct responses.
Multi-Agent Collaboration: Completing a Task in 1 Hour Instead of 1 Week
Bedrock’s new feature helps businesses easily build, deploy, and orchestrate agent teams to write solutions for complex, multi-step tasks.
Using Amazon Bedrock Multi-Agent Collaboration, businesses can create and assign specialized agents to specific project steps to achieve more accurate results and accelerate tasks by coordinating multiple agents working in parallel.
For example, a business can build its own specialized agent on Bedrock and then create supervisory or coordinating agents to manage the other agents.
AWS customers have reported that this multi-agent collaboration reduces tasks that previously took about a week to complete to just one hour.
Model Distillation: Speed Improvements of Up to 500%
Currently, new versions of models are released every week, and businesses need to find the most suitable models based on their actual needs, requiring appropriate expertise, latency, and cost to complete the tasks.
One of the solutions businesses are using right now is model distillation. This involves extracting the data and answers from powerful foundational models to train smaller models. This requires businesses to manage training data and also consider model parameters and weights.

With Amazon Bedrock Model Distillation, customers only need to choose the best model for a given use case and select a smaller model from the same model series. This provides the appropriate cost and latency required for their applications.
Compared to the original models, distillation models can achieve up to a 500% increase in speed, reduce operational costs by 75%, and for use cases like Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG), the accuracy loss is less than 2%.
04. Amazon Q Developer: Going Beyond Code to Cover a Broader Range of Development Tasks
The focus of the latest upgrade to the Amazon Q Developer programming assistance platform is to go beyond code completion and help developers accomplish a wider range of everyday tasks involved in the end-to-end software lifecycle.

New features of Amazon Q Developer include:
Modernizing Windows .NET applications to Linux, achieving 4x speed improvements and reducing licensing costs by up to 40%.
Transforming VMware workloads into cloud-native architectures, with agents automatically planning, authenticating, deciding, and converting network configurations, transforming local network configurations to AWS-equivalent configurations within hours.
Accelerating mainframe modernization by simplifying labor-intensive tasks like code analysis, documentation, planning, and refactoring applications.
Q Developer now automatically generates unit tests and assists developers in writing and maintaining code documentation. It can generate the first code review for developers to use when submitting code. Once the code is in production, Q’s new operational agent automatically pulls data from the company’s monitoring service, AWS CloudWatch, and starts investigating when an alert is triggered.
AWS also introduced an Agent for modernizing COBOL mainframe applications.
Additionally, developers and security platform GitLab announced a collaboration to integrate GitLab's Duo AI assistant with Amazon's Q autonomous Agent. GitLab users can now access many of the Agents offered in Amazon Q Developer via Duo’s chat feature to help with code reviews, generate unit tests, and modernize their Java applications. This feature is now directly integrated into GitLab's chat UI.
05. A 14-Year Partnership with NVIDIA, and the Release of P6 Instances Based on the Blackwell Architecture in Early 2025
AWS provides core services through building blocks, enabling businesses to more easily combine these services and create truly interesting applications. This concept of building blocks has been the foundation of AWS’s service creation and customer support. AWS has already provided a large number of service modules.
For example, in the biological field, AWS developed the ESM model series to help scientists worldwide understand and design proteins. ESM3 has been trained with 1 quadrillion operations and has calculated over 2 billion protein sequences, allowing scientists to design proteins like chips, taking a step towards bio-programmability.
Garman mentioned that a key reason enterprises choose AWS is security. Valuing security is fundamental to how AWS operates its business, impacting how it designs data centers, chips, virtualization stacks, and service architectures.
On top of this, AWS now offers more compute resources than any other vendor. Amazon EC2 has more options, instances, and features, allowing businesses to find the appropriate performance for their workloads.
For instance, if a company is running a large database for analytics, AWS can run the largest storage systems anywhere. If the business is running an HPC cluster, large models, and all clusters, and needs fast networking to connect these components, AWS has the fastest, most skilled network available.
AWS’s self-designed chips offer greater flexibility. By moving the virtualization design in Nitro systems alone, it can eliminate the need to redo the virtualization stack. New instance types allow for quick, easy development.
AWS's Graviton series processors are now widely used by nearly all AWS customers and offer a 40% improvement in cost-performance. Graviton can handle a broader range of workloads, including scalar code and databases.
Currently, most models run on NVIDIA GPUs. AWS and NVIDIA have been collaborating for 14 years. Garman announced an upgrade to their partnership, with the release of P6 instances. The P6 series will use the new Blackwell chips and will be available in early 2025. The P6 instances will offer up to 2 chips, with computing speeds 5 times faster than the current generation of GPUs.
06. Expansion of Amazon S3 Storage Features for Faster Data Lake Analytics and Automated Metadata Generation
AWS is dedicated to offering simple, scalable storage options. Launched in 2006, Amazon S3 fundamentally changed how data is managed, with this service growing explosively over the past decade. Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering has saved customers $4 billion.

Building on this, AWS launched the Amazon S3 Tables feature, making S3 the first fully managed cloud object storage to support Apache Iceberg, enabling faster analytics while simplifying storage and management of tables (Table) data at any scale.
Many customers organize their data for analysis in table format, typically stored in Apache Parquet. Parquet is one of the fastest-growing data types in S3, and Iceberg has become the most popular open table format (OTF) for managing Parquet files.
AWS calls S3 Tables "the easiest and quickest way to analyze Apache Iceberg tables in S3." Built specifically for managing Apache Iceberg tables in data lakes, it is the first cloud object storage with native Apache Iceberg table support and introduces a new bucket type optimized for storing and querying table data in Iceberg format.
Compared to standard S3 buckets, S3 Tables offers 3x the query performance, 10x the transactions per second (TPS), and automatically manages table maintenance tasks.
AWS also launched Amazon S3 Metadata, which can nearly real-time generate queryable target metadata, making it easier to discover and manage vast amounts of data in S3.
S3 Tables (General Availability) and S3 Metadata (Preview) are now available, compatible with Apache Iceberg tables, supporting easy querying using AWS analytics services and open-source tools.
07. Two Major Database Updates: Cross-Region Operations with Strong Consistency
AWS today announced new features for Amazon Aurora DSQL and Amazon DynamoDB global tables to support workloads that demand cross-region operations, strong consistency, low latency, and high availability. The cross-region strong consistency feature for both databases is now in preview.

This year marks the 10th anniversary of Amazon Aurora, the fastest-growing AWS service. Tens of thousands of customers rely on Amazon Aurora daily for the performance of enterprise-grade commercial databases and the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of open-source databases.
Now, AWS is rethinking relational databases, allowing customers to avoid choosing between low latency or SQL.
Amazon Aurora DSQL is a new serverless distributed SQL database that offers all the performance and features of high-end commercial databases while retaining the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of open-source databases.
Compared to other popular distributed SQL databases, Aurora DSQL's read-write speed is up to 4 times faster, multi-region availability is up to 99.999%, scalability is virtually limitless, and there’s no need to manage infrastructure, configure, patch, or manage database instances.
Aurora DSQL overcomes two historical challenges for distributed databases—achieving low-latency strong consistency across regions and synchronizing servers globally with microsecond precision.
The database separates transaction processing from storage and checks each transaction only at commit time, parallelizing writes across all regions on commit to provide a multi-region database with strong consistency and fast writes. All updates and security patches are performed without downtime and with no impact on performance.
To ensure that each region sees database operations in the exact order they occur, Aurora DSQL uses Amazon Time Sync Service, adding a hardware reference clock to each Amazon EC2 instance, synchronized with atomic clocks connected to satellites, providing microsecond-precise time anywhere in the world.
Amazon DynamoDB, the first fully managed serverless NoSQL database, has redefined performance and simplified operations. It remains infrastructure-free at any scale, maintaining single-digit millisecond performance.
It now supports multi-region strong consistency, ensuring customers' multi-region applications always read the latest data without changing any application code.
08. New Data Center Components for High-Density AI Workloads
AWS announced new data center components (power, cooling, hardware design) aimed at supporting high-density AI workloads.
(1) Simplified electrical and mechanical designs to achieve 99.9999% infrastructure availability, reducing the number of racks potentially affected by electrical issues by 89%.
(2) Innovations in cooling, rack design, and control systems: Developing a new configurable liquid cooling solution to maximize power use by optimizing rack positioning and updating standardized monitoring, alarm, and operational sequence control systems.
(3) Improved energy efficiency and sustainability: Compared to previous designs, mechanical energy consumption can be reduced by up to 46% under peak cooling conditions; the carbon footprint in concrete for the data center’s exterior is reduced by 35% compared to industry averages; and backup generators will use biodegradable, non-toxic renewable diesel fuel.
09. Conclusion: A Large-Scale Tech Innovation Showcase
AWS re:Invent has always been a major showcase of innovations in computing, security, storage systems, and AI infrastructure.
Since its launch in the fall of 2003, AWS has continuously lowered the barrier to cloud services, transforming enterprise-scale cost structures and infrastructure into something accessible to everyone. This enables businesses of all sizes to avoid reinventing the wheel in computing, storage, databases, analytics, and more.
With the depth of full-stack innovation and the breadth of its product offerings, this cloud giant continues to strengthen its reputation for performance, energy efficiency, security, compliance, scalability, and its ability to keep up with the rapidly evolving AI demands. AWS’s deep experience and resources help customers focus on their core businesses and adapt to innovation.