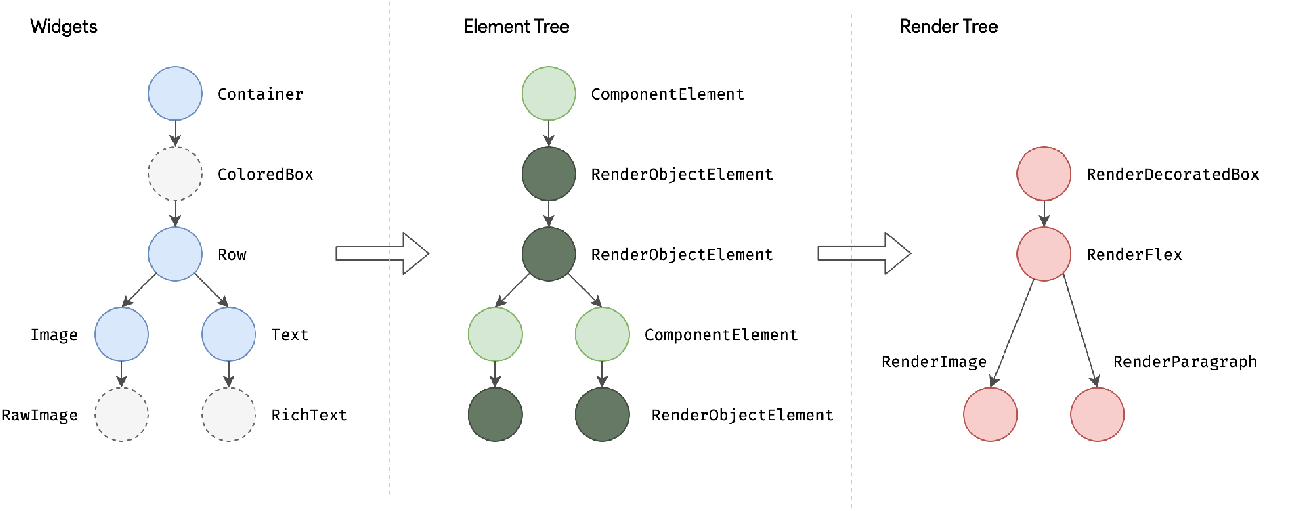
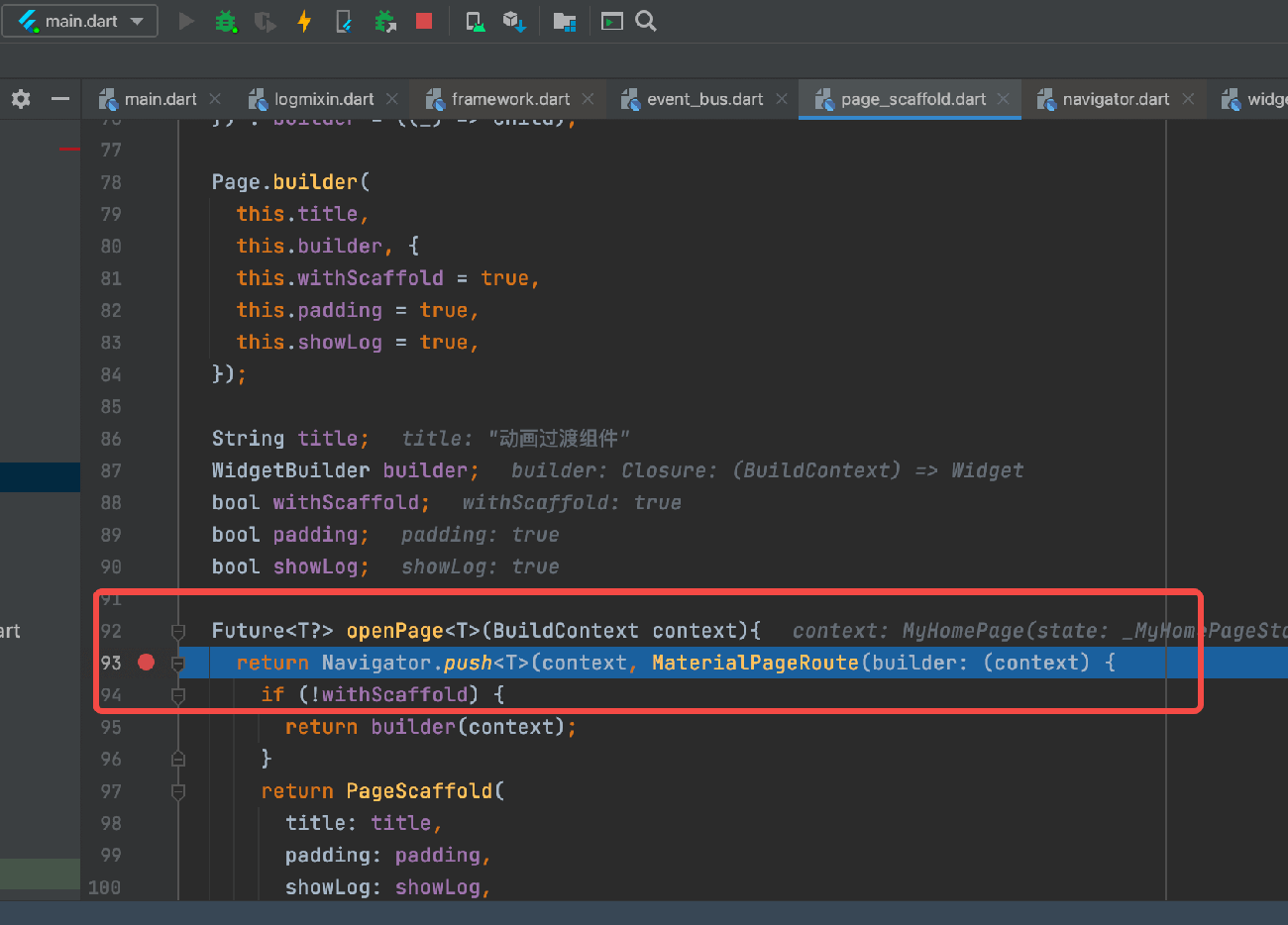
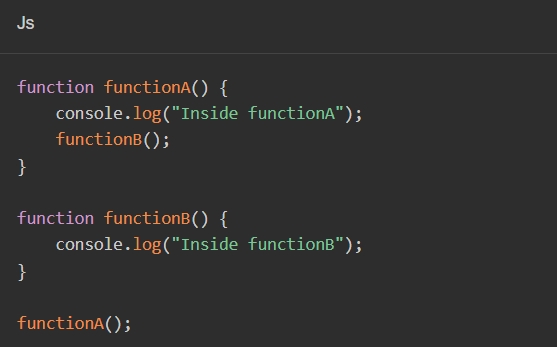
In this example app, both language and theme can be set, and both are implemented using ChangeNotifierProvider: we use Consumer2 in the main function to depend on ThemeModel and LocaleModel. Therefore, when we change the current settings in the language and theme settings pages, the builder for Consumer2 will be re-executed, building a new MaterialApp, so the modifications will take effect immediately. Let’s look at the implementation of the language and theme settings pages.
1 Language Selection Page
The app's language selection page provides three options: Simplified Chinese, American English, and Follow System. We highlight the currently used language in the app and add a checkmark icon next to it, implemented as follows:
import '../index.dart';
class LanguageRoute extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
var color = Theme.of(context).primaryColor;
var localeModel = Provider.of<LocaleModel>(context);
var gm = GmLocalizations.of(context);
Widget _buildLanguageItem(String lan, value) {
return ListTile(
title: Text(
lan,
// Highlight the app's current language
style: TextStyle(color: localeModel.locale == value ? color : null),
),
trailing: localeModel.locale == value ? Icon(Icons.done, color: color) : null,
onTap: () {
// This line of code will notify MaterialApp to rebuild
localeModel.locale = value;
},
);
}
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(gm.language),
),
body: ListView(
children: <Widget>[
_buildLanguageItem("中文简体", "zh_CN"),
_buildLanguageItem("English", "en_US"),
_buildLanguageItem(gm.auto, null),
],
),
);
}
}The logic of the above code is quite simple. The only thing to note is that we defined the _buildLanguageItem(...) method inside the build(...) method. This allows the method to share variables from the context of build(...), in this case, sharing localeModel. However, if the implementation of _buildLanguageItem(...) were more complex, it would be better to define it as a method of the LanguageRoute class. The running effect of this page is shown in Figures :
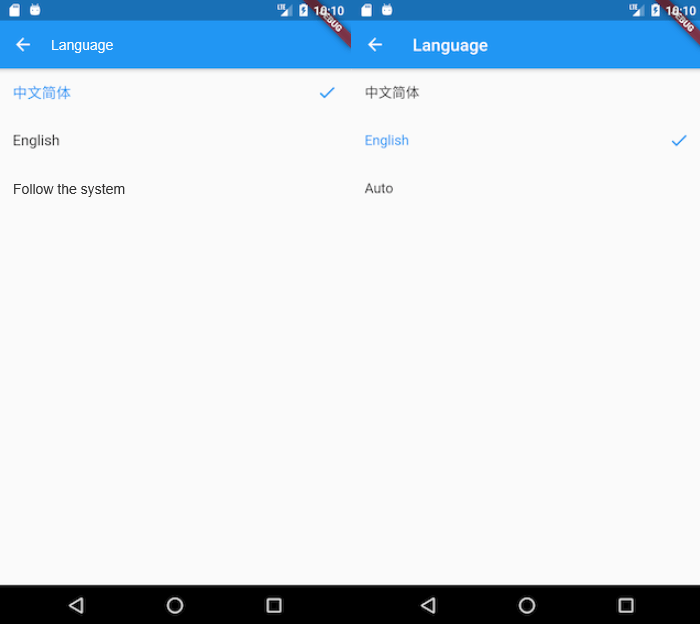
The language switch takes effect immediately.
2 Theme Selection Page
A complete theme includes many options defined in ThemeData. For simplicity, we only configure the theme color in this example. We provide several predefined theme colors for users to choose from, and clicking on a color block updates the theme. The implementation code for the theme selection page is as follows:
class ThemeChangeRoute extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(GmLocalizations.of(context).theme),
),
body: ListView( // Display theme color blocks
children: Global.themes.map<Widget>((e) {
return GestureDetector(
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 5, horizontal: 16),
child: Container(
color: e,
height: 40,
),
),
onTap: () {
// After the theme update, MaterialApp will rebuild
Provider.of<ThemeModel>(context, listen: false).theme = e;
},
);
}).toList(),
),
);
}
}The running effect is shown in Figure :
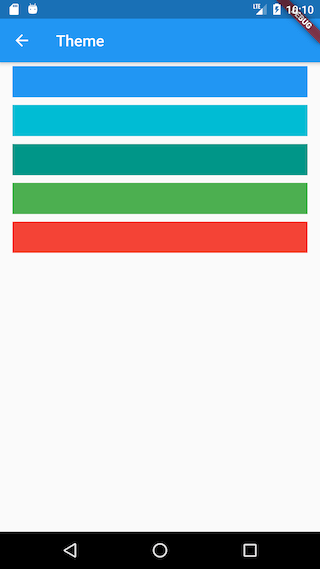
After clicking on another theme color block, the app's theme color switches and takes effect immediately.