30.1 Padding
Padding allows adding spacing (or white space) to its child nodes, similar to the margin effect. We’ve already used it in many examples before, but now let’s take a closer look at its definition:
Padding({
...
EdgeInsetsGeometry padding,
Widget child,
})EdgeInsetsGeometry is an abstract class. In development, we generally use the EdgeInsets class, which is a subclass of EdgeInsetsGeometry and provides some convenient methods for setting padding.
30.2 EdgeInsets
Let's take a look at the convenient methods provided by EdgeInsets:
fromLTRB(double left, double top, double right, double bottom): Specifies padding for each of the four directions individually.all(double value): Uses the same padding value for all directions.only({left, top, right, bottom}): Sets padding for specific directions (you can specify multiple directions at once).symmetric({vertical, horizontal}): Sets padding for symmetrical directions.verticalrefers to top and bottom, whilehorizontalrefers to left and right.
30.3 Example
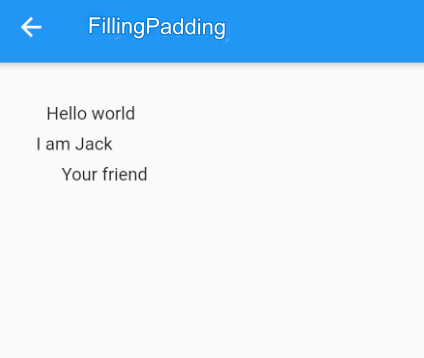
The following example demonstrates the different uses of EdgeInsets. It’s relatively simple, and the source code is as follows:
class PaddingTestRoute extends StatelessWidget {
const PaddingTestRoute({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Padding(
// Adds 16 pixels of padding to all sides
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
// Explicitly align to the left to avoid alignment interference
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: const <Widget>[
Padding(
// Adds 8 pixels of padding to the left
padding: EdgeInsets.only(left: 8),
child: Text("Hello world"),
),
Padding(
// Adds 8 pixels of padding vertically (top and bottom)
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 8),
child: Text("I am Jack"),
),
Padding(
// Adds padding to all four sides individually
padding: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(20, 0, 20, 20),
child: Text("Your friend"),
)
],
),
);
}
}The result is shown in Figure.