51.1 Synchronizing State through Events
In Flutter development, state management is an enduring topic. The general principle is: if the state is private to a component, it should be managed by that component itself; if the state needs to be shared across components, it should be managed by a common parent element of those components. Managing private state for a component is straightforward, but for state shared across components, there are various management approaches. For instance, using a global event bus like EventBus (which will be introduced in the next chapter) implements the observer pattern, enabling state synchronization across components: the state holder (publisher) is responsible for updating and publishing the state, while the state user (observer) listens for state change events to perform certain actions. Below is a simple example of synchronizing login state:
Defining Events:
enum Event {
login,
... // Other events omitted
}The login page code is roughly as follows:
// Publish the state change event after the login state changes bus.emit(Event.login);
Pages that depend on the login state:
void onLoginChanged(e) {
// Logic to handle login state change
}
@override
void initState() {
// Subscribe to login state change events
bus.on(Event.login, onLogin);
super.initState();
}
@override
void dispose() {
// Unsubscribe
bus.off(Event.login, onLogin);
super.dispose();
}We can see that using the observer pattern to implement cross-component state sharing has some obvious drawbacks:
Various events must be explicitly defined, which is cumbersome to manage.
Subscribers must explicitly register state change callbacks and also manually unbind the callbacks when the component is destroyed to avoid memory leaks.
Is there a better way to manage cross-component state in Flutter? The answer is yes! So how can we do it? Let’s think back to the InheritedWidget introduced earlier. Its innate characteristic is the ability to bind the dependencies between the InheritedWidget and its dependent descendant components. When the data of the InheritedWidget changes, it can automatically update the dependent descendant components! Utilizing this feature, we can store the states that need to be shared across components in the InheritedWidget, and then reference it in the child components. The well-known Provider package in the Flutter community is based on this concept and provides a solution for cross-component state sharing. Next, we will introduce the usage and principles of Provider in detail.
51.2 Provider
Provider is an official state management package for Flutter. To enhance readers' understanding of its principles, instead of directly looking at the source code of the Provider package, I will guide you step by step to implement a minimally functional Provider based on the approach described above using InheritedWidget.
1. Implementing Your Own Provider
First, we need an InheritedWidget that can store shared data. Since the specific business data types are unpredictable, we will use generics to define a generic InheritedProvider class that extends InheritedWidget:
// A generic InheritedWidget to store state that needs to be shared across components
class InheritedProvider<T> extends InheritedWidget {
InheritedProvider({
required this.data,
required Widget child,
}) : super(child: child);
final T data;
@override
bool updateShouldNotify(InheritedProvider<T> old) {
// Simply return true to trigger `didChangeDependencies` for dependent descendant nodes on every update.
return true;
}
}Now that we have a place to store the data, we need to rebuild the InheritedProvider when the data changes. This brings us to two questions:
How to notify when the data changes?
Who will rebuild the
InheritedProvider?
The first question is quite straightforward. We could use the event bus introduced earlier for event notification, but to align more closely with Flutter development, we will use the ChangeNotifier class provided in the Flutter SDK. ChangeNotifier extends Listenable and implements a Flutter-style publisher-subscriber pattern. The definition of ChangeNotifier is roughly as follows:
class ChangeNotifier implements Listenable {
List listeners = [];
@override
void addListener(VoidCallback listener) {
// Add listener
listeners.add(listener);
}
@override
void removeListener(VoidCallback listener) {
// Remove listener
listeners.remove(listener);
}
void notifyListeners() {
// Notify all listeners, triggering their callbacks
listeners.forEach((item) => item());
}
... // Other irrelevant code omitted
}We can add or remove listeners (subscribers) by calling addListener() and removeListener(), and we can trigger all listener callbacks by calling notifyListeners().
Now, we will place the state we want to share into a Model class and make it extend ChangeNotifier. This way, when the shared state changes, we only need to call notifyListeners() to notify subscribers, which also answers the second question! Next, we will implement this subscriber class:
class ChangeNotifierProvider<T extends ChangeNotifier> extends StatefulWidget {
ChangeNotifierProvider({
Key? key,
this.data,
this.child,
});
final Widget child;
final T data;
// A convenience method for widgets in the subtree to access shared data
static T of<T>(BuildContext context) {
final type = _typeOf<InheritedProvider<T>>();
final provider = context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<InheritedProvider<T>>();
return provider.data;
}
@override
_ChangeNotifierProviderState<T> createState() => _ChangeNotifierProviderState<T>();
}This class extends StatefulWidget and defines a static method of() for subclasses to easily access the shared state (model) stored in the InheritedProvider. Next, we will implement the corresponding _ChangeNotifierProviderState class:
class _ChangeNotifierProviderState<T extends ChangeNotifier> extends State<ChangeNotifierProvider<T>> {
void update() {
// If the data changes (the model class calls notifyListeners), rebuild the InheritedProvider
setState(() => {});
}
@override
void didUpdateWidget(ChangeNotifierProvider<T> oldWidget) {
// When the Provider updates, if the new and old data are not equal, unbind the old data listener and add the new data listener
if (widget.data != oldWidget.data) {
oldWidget.data.removeListener(update);
widget.data.addListener(update);
}
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
}
@override
void initState() {
// Add a listener to the model
widget.data.addListener(update);
super.initState();
}
@override
void dispose() {
// Remove the model's listener
widget.data.removeListener(update);
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return InheritedProvider<T>(
data: widget.data,
child: widget.child,
);
}
}The main purpose of the _ChangeNotifierProviderState class is to rebuild the widget tree when the shared state (model) changes. Note that when calling the setState() method in the _ChangeNotifierProviderState class, the widget.child is always the same. Therefore, when executing build, the child referenced by InheritedProvider remains the same widget, so widget.child does not trigger a rebuild, effectively caching the child! However, if the parent widget of ChangeNotifierProvider rebuilds, the child passed to it may change.
Now that we have completed the necessary utility classes, let's look at how to use these classes through a shopping cart example.
2. Shopping Cart Example
We need to implement a feature that displays the total price of all items in the shopping cart:
Update the total price when a new item is added to the cart.
Define an Item class to represent item information:
class Item {
Item(this.price, this.count);
double price; // Price per item
int count; // Quantity of items
//... Other properties omitted
}Define a CartModel class to save the item data in the shopping cart:
class CartModel extends ChangeNotifier {
// List to store items in the shopping cart
final List<Item> _items = [];
// Prevents modification of item information in the cart
UnmodifiableListView<Item> get items => UnmodifiableListView(_items);
// Total price of items in the cart
double get totalPrice =>
_items.fold(0, (value, item) => value + item.count * item.price);
// Adds [item] to the cart. This is the only way to modify the cart from the outside.
void add(Item item) {
_items.add(item);
// Notify listeners (subscribers) to rebuild the InheritedProvider and update the state.
notifyListeners();
}
}CartModel is the model class that needs to be shared across components. Finally, we construct the example page:
class ProviderRoute extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_ProviderRouteState createState() => _ProviderRouteState();
}
class _ProviderRouteState extends State<ProviderRoute> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: ChangeNotifierProvider<CartModel>(
data: CartModel(),
child: Builder(builder: (context) {
return Column(
children: <Widget>[
Builder(builder: (context) {
var cart = ChangeNotifierProvider.of<CartModel>(context);
return Text("Total Price: ${cart.totalPrice}");
}),
Builder(builder: (context) {
print("ElevatedButton build"); // Used in later optimization
return ElevatedButton(
child: Text("Add Item"),
onPressed: () {
// Add item to the cart, total price will update after addition
ChangeNotifierProvider.of<CartModel>(context).add(Item(20.0, 1));
},
);
}),
],
);
}),
),
);
}
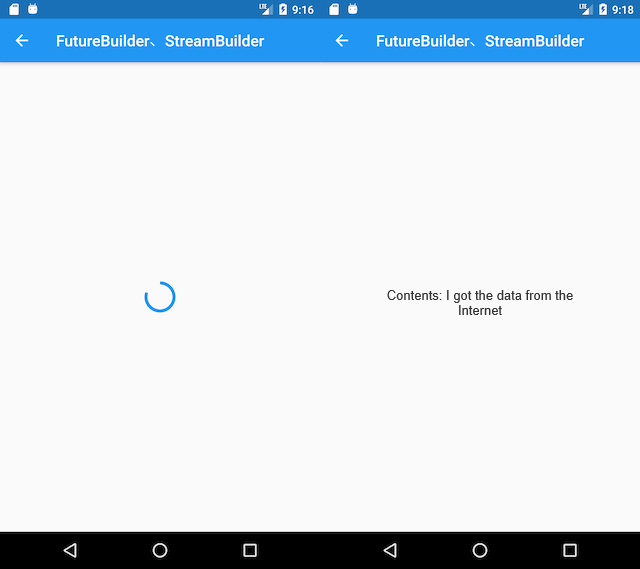
}After running the example, the effect is shown in Figure:
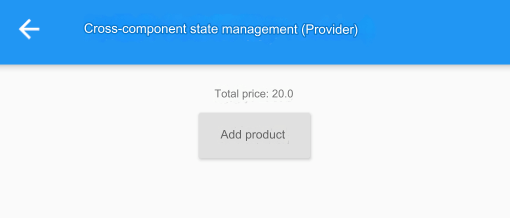
Every time the "Add Item" button is clicked, the total price increases by 20, and we have achieved the desired functionality! Some readers may wonder if it's meaningful to go through such a roundabout way to implement such a simple feature. In fact, for this example, we are only updating a state within the same route page, and the advantages of using ChangeNotifierProvider are not very evident. However, what if we are building a shopping app? Since shopping cart data is typically shared throughout the app, for instance, across routes, if we place ChangeNotifierProvider at the root of the entire application widget tree, then the entire app can share the shopping cart data. This is where the advantages of ChangeNotifierProvider become very clear.
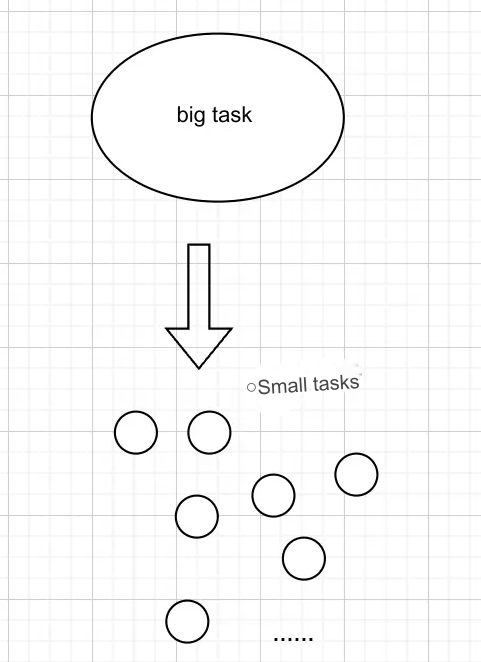
Although the above example is relatively simple, it clearly illustrates the principles and processes of Provider. Figure shows the principles of Provider:
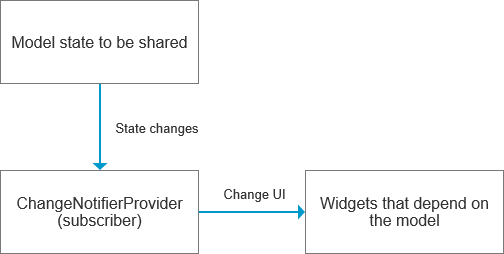
When the model changes, it automatically notifies the ChangeNotifierProvider (the subscriber), which then rebuilds the InheritedWidget. The descendant widgets that depend on this InheritedWidget will update accordingly.
We can see that using Provider will bring the following benefits:
Our business logic focuses more on the data. As long as the model is updated, the UI will automatically refresh without needing to explicitly call
setState()after the state changes.The message passing for data changes is abstracted away. We no longer need to manually handle the publication and subscription of state change events; everything is encapsulated within
Provider. This is truly great and saves us a lot of work!In large, complex applications, especially those with many globally shared states, using
Providerwill significantly simplify our code logic, reduce the likelihood of errors, and improve development efficiency.
51.3 Optimization
The ChangeNotifierProvider we implemented above has two obvious drawbacks: code organization issues and performance issues. Let's discuss these one by one.
1. Code Organization Issues
Let's take a look at the code that builds the total price Text:
Builder(builder: (context) {
var cart = ChangeNotifierProvider.of<CartModel>(context);
return Text("Total Price: ${cart.totalPrice}");
})This piece of code has two points that can be optimized:
It requires explicitly calling
ChangeNotifierProvider.of, which becomes quite redundant when many widgets depend onCartModelwithin the app.The semantics are unclear; since
ChangeNotifierProvideris a subscriber, any widget that depends onCartModelis naturally a subscriber and a consumer of the state. If we useBuilderfor this purpose, the semantics are not very clear. If we could use a widget with clear semantics, such as one calledConsumer, the final code would have much clearer semantics—just by seeingConsumer, we would know it depends on some cross-component or global state.
To optimize these two issues, we can encapsulate a Consumer widget, implemented as follows:
// This is a convenient class that gets the current context and the specified data type's Provider
class Consumer<T> extends StatelessWidget {
Consumer({
Key? key,
required this.builder,
}) : super(key: key);
final Widget Function(BuildContext context, T? value) builder;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return builder(
context,
ChangeNotifierProvider.of<T>(context),
);
}
}The implementation of Consumer is very straightforward. It specifies the template parameter and automatically calls ChangeNotifierProvider.of internally to retrieve the relevant model. Moreover, the name Consumer itself carries a precise meaning (consumer). Now the previous code block can be optimized as follows:
Consumer<CartModel>(
builder: (context, cart) => Text("Total Price: ${cart.totalPrice}"),
)Isn't it elegant!
2. Performance Issues
The above code has a performance issue at the part where the "Add Button" is constructed:
Builder(builder: (context) {
print("ElevatedButton build"); // Log output during construction
return ElevatedButton(
child: Text("Add Item"),
onPressed: () {
ChangeNotifierProvider.of<CartModel>(context).add(Item(20.0, 1));
},
);
})When we click the "Add Item" button, the total price of the items in the cart changes, so updating the text displaying the total price is as expected. However, the "Add Item" button itself does not change and should not be rebuilt. Yet, when we run the example, every time we click the "Add Item" button, the console outputs the log "ElevatedButton build." This means that the "Add Item" button is being rebuilt every time it is clicked! Why is this happening? If you understand the update mechanism of InheritedWidget, the answer becomes clear: This is because the Builder constructing the ElevatedButton calls ChangeNotifierProvider.of, creating a dependency on the InheritedWidget (i.e., InheritedProvider) above in the widget tree. Therefore, when an item is added and the CartModel changes, it notifies the ChangeNotifierProvider, which then rebuilds the subtree. Consequently, the InheritedProvider will update, and any descendant widgets that depend on it will also be rebuilt.
Now that we understand the cause of the issue, how can we avoid this unnecessary reconstruction? Since the button is being rebuilt due to its dependency on the InheritedWidget, we just need to break or remove this dependency. But how can we do that? As mentioned in the previous section about InheritedWidget, the difference between calling dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType() and getElementForInheritedWidgetOfExactType() is that the former registers a dependency, while the latter does not. Therefore, we only need to modify the implementation of ChangeNotifierProvider.of as follows:
// Add a listen parameter indicating whether to establish a dependency
static T of<T>(BuildContext context, {bool listen = true}) {
final type = _typeOf<InheritedProvider<T>>();
final provider = listen
? context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<InheritedProvider<T>>()
: context.getElementForInheritedWidgetOfExactType<InheritedProvider<T>>()?.widget
as InheritedProvider<T>;
return provider.data;
}Then we change the calling part of the code to:
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Consumer<CartModel>(
builder: (BuildContext context, cart) => Text("Total Price: ${cart.totalPrice}"),
),
Builder(builder: (context) {
print("ElevatedButton build");
return ElevatedButton(
child: Text("Add Item"),
onPressed: () {
// Set listen to false to avoid establishing a dependency
ChangeNotifierProvider.of<CartModel>(context, listen: false).add(Item(20.0, 1));
},
);
})
],
)After modifying and running the example again, we will find that clicking the "Add Item" button no longer outputs "ElevatedButton build" in the console, meaning the button will not be rebuilt. Meanwhile, the total price will still update because the value of listen is true by default when calling ChangeNotifierProvider.of in Consumer, so the dependency will still be established.
At this point, we have implemented a mini Provider, which possesses the core functionalities of the Provider Package available on Pub. However, our mini-version is not comprehensive; it only implements a ChangeNotifierProvider that can be listened to and does not implement a provider solely for data sharing. Additionally, our implementation does not consider certain boundaries, such as how to ensure that the model remains a singleton when the widget tree is rebuilt. Therefore, it is recommended that readers use the Provider Package in practical applications, while the main purpose of implementing this mini-provider in this section is to help readers understand the underlying principles of the Provider Package.
51.4 Other State Management Packages
The Flutter community now has many packages specifically for state management. Here are a few that are relatively well-rated:
| Package Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Provider & Scoped Model | Both packages are based on InheritedWidget, and their principles are similar. |
| Redux | The Flutter implementation of the Redux package from the React ecosystem in web development. |
| MobX | The Flutter implementation of the MobX package from the React ecosystem in web development. |
| BLoC | The Flutter implementation of the BLoC pattern. |
I do not recommend any of these packages here; readers interested can research them to understand their respective philosophies.
51.5 Summary
In this section, we introduced some drawbacks of the event bus in cross-component sharing, leading to the idea of using InheritedWidget for state sharing. Based on this idea, we implemented a simple Provider and explored the registration and update mechanisms of InheritedWidget and its dependencies in depth. By studying this section, readers should achieve two goals: first, to thoroughly understand InheritedWidget, and second, to grasp the design philosophy of Provider.
InheritedWidget is a crucial widget in Flutter, and features such as internationalization and themes are implemented using it. Hence, we dedicated several sections to introduce it. In the next section, we will introduce another component based on InheritedWidget: Theme.